The complete guide to maximizing thyroid hormone production to lose weight and look better!
"The first time I took enough desiccated thyroid to make my heart speed noticeably, there was a pleasurable pushing up from my abdomen through my chest, making me want to smile and laugh." Ray Peat
Maximizing your natural production of thyroid will help you become lean and energetic in a healthy way.
T3 and T4 are the center of thyroid hormones that will improve the quality of your life dramatically.
Furthermore, Thyroid hormone aids in:
Normal Hair growth
Normal eyebrow growth
Increasing Body Temperature
Regulating our Metabolic Rate and how many calories we burn
Regulating the rate and strength of heartbeat
Allowing normal breakdown of carbs and fats
Improving your outlook on life - optimism
Better mood
Higher energy and childlike playfulness
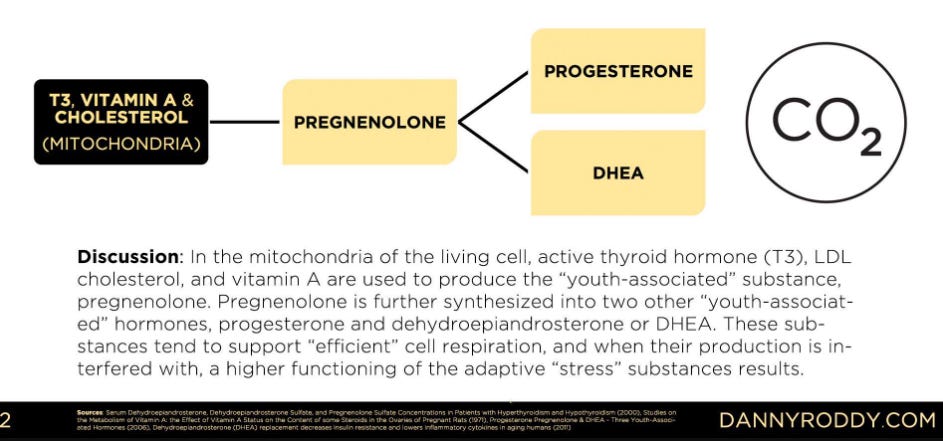
Allowing production of the youth steroid hormones “pregnenolone”, “progesterone, “DHEA”
And the list goes on and on..
If you really want to enjoy life with high energy, optimising thyroid is one of the first places to start.
Let’s geek out a little
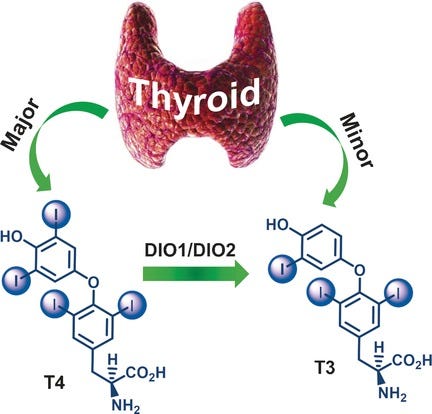
Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3) are synthesized in the thyroid gland, where a large amount of peripheral conversion occurs in the liver (such as from T4 to T3) contributing to the overall T3 levels.
T3 and T4 are then bound to thyroid-binding globulin (TBG) or albumin, that prevents detoxification of thyroid hormones and transports them around in the blood.
T3 and T4 bind to thyroid hormone receptors to exert their metabolic effect. T4 can be converted to T3 via the enzyme deiodinase type 1 (D1), which is an essential step for T3 production (active thyroid hormone).
Furthermore, T3 can be converted back to T4 via the enzyme iodothyronine deiodinase type 2 (D2), but this is not a major conversion pathway.
Side effects of hypothyroidism (low thyroid):
Cold hands and feet and general cold intolerance
Temperatures are below 37C or 98.6F
Heart rate are below 70bpm
Exaggerated stress response – heart rate speeds up like crazy, shaking, sweating, inner tension, nervousness etc.
Hair loss
Losing the outer part of eyebrow
Feeling sluggish and being tired all the time. Can even experience chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS).
Cognitive problems, such as depression, anxiety, slow cognition, little cognitive flexibility, not being open-minded, ridged thinking, etc.
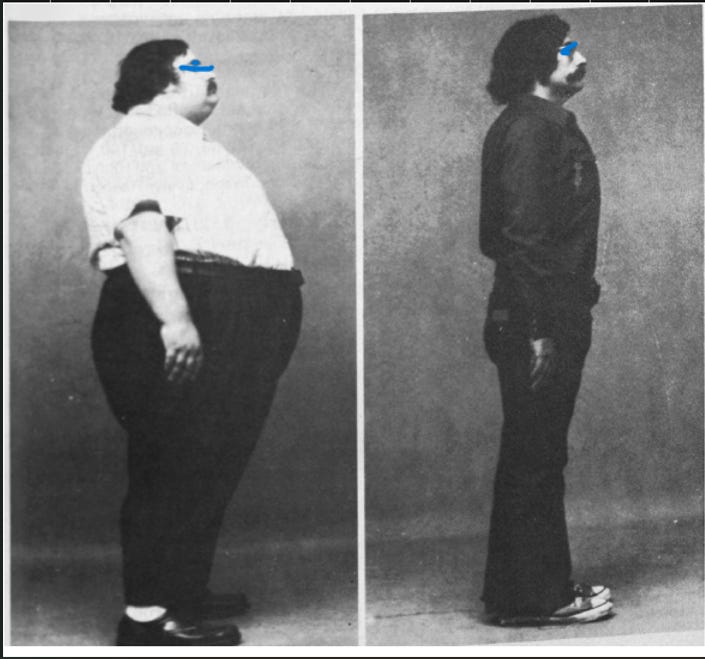
Fat gain and obesity
Metabolic syndrome
Constipation
Diabetes
Bipolar depession
Neurodegenerative disease
Poor Peripheral Circulation (Pale facial skin, cold hands, cold feet etc)
Rapid Premature aging
Migraines
Chronic infection
Cardiovascular disease
Inflammation and chronic illness
Elevated cholesterol and triglycerides
Decreased libido
Edema and Swelling
Muscle aches, frequent cramps, weakness and even fibromyalgia
Slow reflexes. Muscle tranction and relaxation is slow.
And again, the list goes on…
Thyroid is really an amazing hormone to have maximized for overall well-being and reaching the great goals you have set for yourself.
In this article I’m going to show you how to increase your thyroid hormones and I’m going to start with the simple and easy things you can, or rather, must do on a daily basis and then I’m going to go over a few supplements and herbs you can use to boost T3
Here we go, please enjoy, my go to guide/manual for boosting thyroid hormones!
#1 Eat healthy fats
And when I’m saying healthy fats, I’m not talking about canola oil, avocado oil, sunflower oil or any other vegetable, seed or nut oil.
I’m talking about fats that are high in saturated fat.
Fat sources such as beef, buffalo,lamb, goat, game, lean fish, dairy, coconuts and eggs.
The fats found in these sources will have the greatest thyroid boosting effect, because saturated fatty acids (SFAs) are positively associated with thyroid, monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) are more or less neutral whereas polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are will lower thyroid hormones and inhibit the enzymes that produce T4 and T3. Shocking, I know.
The shorter chain fats are burned quickly for energy production, whereas longer SFAs will be built into cell membranes and will make cells more stable. More stable cells, which are less fluid and more compact, are more resilient to stressors, produce less inflammation, are more insulin sensitive, produce more energy,etc.
Eliminating PUFAs are impossible apart from eating a laboratory-made diet and who wants to do that? (A few comes to mind lol).
Sticking to natural organicc foods that are high in saturated fat, such as those mentioned above, and staying away from factory produced foods will dramatically help to lower the intake of rancid oil and inflammation associated with them (PUFAs).
Foods to stay away from include:
Salad dressings
Mayonnaise
All baked and fried goodies
All seed oils
Canned food in oil
Packages food (a lot of them are coating with vegetable oils)
Peanut butter and other nut butter
Foods with 10+ Ingredients
#2 Maximise sleep
Sleep is the most important thing you can do for your health, androgens, health, recovery, muscle growth, brain, etc.
Studies shows that accumulative sleep loss, sleeping less than 7 hours per night repeatedly, lowers T3 and increases serotonin and cortisol.
Sleep loss leads to catabolism of the whole body and the tissue that is destroyed first is the brain, kidney, thymus, spleen, adrenals, muscles and bone. Deterioration also happens in the pancreas and liver, which leads to diabetes, liver disease, indigestion, bowel disorders, etc.
To prevent premature-aging and castration induced by sleepless nights, we need to maximize sleep duration and quality of those hours spent sleeping.
A few tips to improve sleep are:
Sleep in a completely dark room. Get blackout curtains.
Sleep in a completely quiet room.
Block blue light at night.
Do deep tissue lymphatic massages before bed. Deep tissue massage will activate the parasympathetic nervous system and promote sleep.
Get morning sunlight on your eyeballs (not through glass).
Sleep in a cool room. Body temperature needs to drop for you to sleep peacefully.
Turn all wifi and power off in the house to eliminate EMF and electricity.
Be active during the day. I’ve found that when I sprinkle activity, such as intense rope jumping and long works throughout my day, my energy, focus and sleep is better in every way.
#3 Exercise
We should all know by now that exercise is good for us. But we don’t have to slave away in the gym for hours just to get the benefit. On the contrary, training too much can actually lower thyroid hormone and have no extra benefit-by increasing cortisol and adrenaline.
A short 15-30 minutes heavy and explosive weight training session will suffice. A longer workout up to 90 minutes will also be effective, but the benefits seem to drop off from there. So there is a bell curve, at one point, you need about 15+ minutes for a proper stimulus and then on the other end, benefits drop of at 90 minutes.
Also, adding in too much cardio to your training will have a negative effect on your recovery ability as it increases catabolism and increases cortisol,estrogen etc.
#4 Lower Estrogen
Inhibit aromatase (the enzyme that converts testosterone to estrogen) as estrogen is one of the most potent inhibitors of thyroid hormone production,conversion and utilisation.
Things that lower estrogen and inhibit aromatase:
-DHT
-Sunlight
-Coffee
-White button mushrooms
-Zinc
-Vitamin E
-Vitamin K2
#5 Lower Prolactin
Prolactin suppresses cAMP production, potentially by enhancing phosphodiesterase activity. Additionally, prolactin decreases 5-alpha reductase levels and reduces DHT which increases estrogen.
Vitamin B6 lowers prolactin which I talk about later in this article.
#6 Lower stress
Stress is incredibly common these days and seems almost impossible to avoid apart from moving to the forest and staying out of society. But that is definitely not a practical option for most of us, or not that we even want to do that, so we have to look at other options to keep stress at bay.
Stress stimulates the adrenal glands to secrete cortisol and catecholamines, such as noradrenaline and adrenaline, all of which are pretty beneficial and harmless if it only happens in the short term.
But chronic stress is very harmful to the body and will lower the metabolism, T4 and T3 production and increase the aromatase - a negative feedback cycle which we don’t want.
A few simple ways to destress are:
Take a moment to breathe. Inhale deeply and slowly using your diaphragm, allowing your stomach to expand forward and sideways, while keeping your chest still. Quick, shallow breaths caused by stress, fatigue, or poor posture can trigger your body's stress response. By sitting or standing up straight with your shoulders relaxed, you can breathe more fully and peacefully. Inhale for four seconds and exhale for eight seconds. After about four breaths, you should start to feel significantly more relaxed. As you breathe, concentrate on something uplifting.
Take a walk somewhere, ideally in nature or somewhere with less pollution
Get your posture right - Hunching over and maintaining low power poses lowers testosterone,T3 and increases cortisol
Laughter - People who laugh more tend to have lower cortisol, higher dopamine, stronger immunity and have a better sense of well-being
Ensure your blood sugar stays balanced throughout the day
#7 Improve insulin sensitivity
Insulin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in signaling energy intake and boosting T3 production. It is essential for transporting glucose into cells, where it is oxidized to generate ATP, which is necessary for thyroid hormones.
Among monosaccharides, glucose has the highest potential to stimulate insulin release, and certain amino acids can also significantly elevate insulin levels. It's important not to consume protein alone (following the 2:1 rule mentioned earlier), as this can lead to hypoglycemia, prompting an increase in glucagon and cortisol to restore blood glucose levels.
While aiming for hyperinsulinemia isn't ideal, it's important to maintain insulin sensitivity to enable insulin's pro-steroidogenic and anabolic effects.
Here are some strategies to enhance insulin sensitivity:
Reduce cortisol levels.
Lower excessive free fatty acids by taking niacinamide - consider using 500 mg of niacinamide with each high-carb meal.
Engage in 30 seconds of high-intensity exercise before your high-carb meal; I prefer doing some running up and down the stairs
Take a 10 to 20-minute walk after meals.
Avoid excessive vegetable and seed oils.
Steer clear of junk food in general.
Aim for adequate sleep.
#8 Use natural products
Chemical products, including hand soap, shampoo, shaving cream, aftershave, deodorant, lotion, and others, often contain endocrine-disrupting chemicals.
There are thousands of these substances, each with the potential to interfere with normal cellular function.
Here are a few alternatives:
A natural bar soap, like coconut oil bar soap, can be used for washing your body and hair, and even for shaving. If you use a shaving brush, you can create a rich lather for shaving.
Castile soap is a versatile option suitable for washing your hands, body, hair, and even laundry.
#9 Eat natural and organic foods
Pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides can all disrupt gut health, harm overall well-being, and lower T3 levels.
Natural foods like cocoa powder, various fruits (such as berries, apples, pomegranates, oranges, and guavas), and raw milk can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation while promoting T3 production. These foods are rich in antioxidants and nutrients that support overall health and hormonal balance.
#10 Stay away from plastics
Plastics are another significant source of endocrine disruptors, and the increasing pollution of our environment with plastics makes it increasingly vital to avoid them. Plastics are not limited to products we use but are also present in the air we breathe, the water we drink and bathe in, and potentially even in the food we consume, as soils become contaminated with plastics.
To begin with, it's important to reduce or eliminate your use of plastics, such as plastic bottles, Tupperware, cling film, and utensils and to avoid touching receipts etc
#11 Increase dopamine
Dopamine, which quite the opposite of serotonin actually increases total and free thyroid levels, High dopamine is associated with creativity, exploration, happiness, open-mindedness, motivation, etc.
#12 Get plenty of sunlight
Bright light exposure improves T4 uptake into cells, which reduces hypothyroid symptoms. Interestingly, bright light was better than exercise at relieving seasonal mood disorders.
This study found that in winter, bright light exposure was associated with a significantly greater reduction in TSH and anger, a significantly greater increase in free T3 and a smaller increase in depressive symptoms when compared with dim light.
Bright light has also been shown to decrease rT3, which means that thyroid hormone uptake into the cells is increased - which is a good thing.
#13 Avoid heavy metals
Heavy metals like mercury, cadmium, and arsenic are extremely harmful to health. They can lead to a decrease in thyroid levels and are linked to issues such as insulin resistance, obesity, diabetes, and psychiatric disorders(anxiety,depression,schizophrenia etc). Additionally, toxic heavy metals can elevate aromatase levels, which in turn increases estrogen.
By the way, I teach all of this in T3 Optimisation
#14 Lower Cortisol
Chronically elevated cortisol: Increases the aromatase and can lead to estrogen dominance and inhibits thyroid function by lowering TRH, TSH and also the conversion of T4 to T3.
A few simple tricks to lower it:
Eat carbs
Eat Saturated Fats
Walk in Nature
#15 Eat foods high in Zinc
Zinc lowers cortisol, prolactin and estrogen which prevents the blockage of proper thyroid hormone production,conversion and utilisation.
#16 Fix your gut health
Nothing is the body works in isolation and with that being said, whatever negatively influences the gut, can have a negative effect on the thyroid.
The thyroid gland requires specific micronutrients to function properly, produce hormones, and execute their effects throughout the body. These micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are cruical for thyroid hormone synthesis, conversion, and cellular function.
So what does the gut have to do with this?
Inadequate micronutrient consumption and gut inflammation can lead to impaired thyroid function. The gut's villi, responsible for absorption, can be damaged due to inflammation, reducing micronutrient absorption.
Key Micronutrients for Thyroid Health:
Focus on the following essential micronutrients for thyroid health:
Iron and copper (for thyroid hormone synthesis)
Selenium and zinc (for T4 to T3 conversion)
Vitamin A and D (for immune regulation)
Restoring Gut Health and Micronutrient Balance:
To address thyroid function, it's crucial to:
Eliminate inflammatory foods (gluten, lectins, refined grains, etc.)
Restore gut integrity and function
Load up on essential micronutrients
#17 Reduce Endotoxin
Endotoxins, also known as Lipopolysaccharides, are found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. They are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide composed of O-antigen, outer core and inner core joined by a covalent bond. Different bacteria can create different kinds of endotoxins, some being much more inflammatory than others.
Endotoxins can antagonize thyroid function in many ways:
-Endotoxins inhibit the conversion of T4 into T3, by suppressing the enzyme, type 1 iodothyronine deiodinase (D1)
-Endotoxins have been shown to decrease the expression of thyroid receptors, specifically in the liver
You have now understood that we don’t want pesky endotoxins in our system. The best way to lower endotoxins is to lower gram-negative bacteria (specifically the Enterobacteriaceae group) and you can do this by increasing transit time, lowering gut inflammation and using organic raw honey.
#18 Enjoy some coffee
Coffee drinkers have a lower incidence of thyroid disease, including cancer, thannon-drinkers. Caffeine has remarkable parallels to thyroid and progesterone, caffeine tends to activate thyroid secretion by a variety of mechanisms, increasing cyclic AMP and decreasing serotonin in thyroid cells - a hidden superfood.
#19 Eat foods high in Iodine
The thyroid gland needs iodine to create T4. In fact, the four in the shortening refers to 4 molecules of iodine. Not only that but the symporter mechanism that draws iodine into the thyroid gland requires B-vitamins and vitamin C to function normally.
I would recommend getting iodised salt as an easy source of iodine or high quality potatoes for an iodine source.
#20 Avoid inhibitory foods
Certain foods can negatively impact thyroid hormone production, particularly when consumed on a low-iodine diet.
Examples of such foods include:
Soy
Foods high in goitrogens
Bamboo Shoots
#21 Avoid these inhibitory chemicals and drugs
Synthetic chemicals can interfere with thyroid hormone production, conversion, and function. As a result, even if thyroid hormone levels are sufficient, exposure to these endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) can still cause hypothyroid symptoms.
A list of these chemicals include:
BPA (found in plastic)
Phthalates
Pesticides
Arsenic
Cadmium
Lead
Mercury
Herbicides
That’s it for diet and lifestyle changes, let’s talk supplements and herbs.
#1 Black Seed
In just 8 weeks, 2 grams of Nigella sativa seed powder (Black seed) lead to significant reductions in BMI, IL-23 levels, TSH, and anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO), while also elevating serum T3 levels.
Black seed is also famously known as the “cure for every disease except death”
It’s also high in thymoquinone - a powerful quinone that boosts metabolism and lowers oxidative stress.
#2 Selenium
Selenium is a very important mineral for the enzyme deiodinase 2, which converts thyroid hormone T4 to T3.
Selenium is also a powerful antioxidant.
#3 Vitamin A
Vitamin A is essential for a healthy hormonal balance as well as good eye, teeth, skin and immune function.
Vitamin A protects the body from the negative effects of estrogen excess which is detrimental for proper thyroid function.
Foods high in vitamin A - chicken liver, ghee, butter, cheese, eggs, and milk.
#4 Boron
Many studies show that boron can effectively lower estrogen hence improving thyroid function.
Dried fruit such as raisins and dates are also in boron.
#5 Calcium
People with the highest calcium intake had the lowest levels of estrogen. High calcium consumption appears to suppress parathyroid hormone (PTH), which in turn inhibits thyroid function and is associated with inflammatory and catabolic processes.
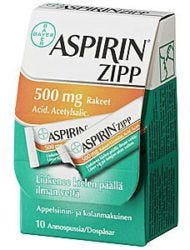
#6 Aspirin
Aspirin is anti-stress, anti-inflammatory, pro-metabolic and last but not least, pro-thyroid.
Aspirin also shifts the mitochondria from the state of oxidizing fats into oxidizing glucose, which is favorable for thyroid function,.
Aspirin is also an estrogen antagonist and prevents the lipid peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) both of which are favorable things for thyroid health. However, aspirin thins the blood so use cautiously.
“Since aspirin’s effects on the mitochondria are similar to those of T3, using both of them might improve brain energy production more than just thyroid”. - Dr. Ray Peat
#7 Vitamin E
Vitamin E is an estrogen antagonist in high doses, which inhibits the aromatase, and it’s very effective at lowering prolactin - which in turn helps with thyroid function
#8 Vitamin B1
Vitamin B1 lowers serotonin and this will automatically increase thyroid hormone.
Vitamin B1 is also rapidly depleted during stress which rapidly increases your requirements for this vitamin.
#9 Niacinamide
Vitamin B3, particularly in the form of niacinamide, enhances NAD levels and increases the ratio of NAD to NADH. A high NAD ratio is essential for proper thyroid hormone utilisation.
#10 Magnesium
Significantly low serum magnesium levels are correlated with a higher incidence of positive thyroid antibodies (TGAb), as well as an increased prevalence of Hashimoto's thyroiditis and hypothyroidism.
#11 Copper
A copper deficiency has been shown to lead to low thyroid hormone levels in rams, and copper is known to increase androgen receptor expression.
Excellent dietary sources of copper include beef liver, cocoa, oysters, and kale.
#12 Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 has been shown to reduce levels of prolactin and TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone). This effect may be due to it’s ability to decrease excess TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone), which is responsible for stimulating the release of TSH and prolactin
Vitamin B6 is richly found in milk, meat, and organ meats.
If you want to take it further:
T3 optimisation guide: The complete guide to maximizing thyroid hormone production to lose weight and look more attractive - Click here to join and optimise your T3.
References:
https://www.healio.com/news/endocrinology/20210818/foods-with-high-protein-saturated-fatty-acids-linked-to-better-thyroid-function
https://raypeat.com/articles/articles/caffeine.shtml
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6321217/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29904828/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12370839/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21745527/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20685100/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12000205/
The adenylyl cyclase-cAMP pathway contributes to kynurenine-induced vessel relaxation. : Kynurenine is an endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced during inflammation : Nature Medicine : Nature Research. Nature.com Journal.
Meikle A. The interrelationships between thyroid dysfunction and hypogonadism in men and boys. Thyroid. 2004;14 Suppl 1:S17-25
Silva J. The multiple contributions of thyroid hormone to heat production. J Clin Invest. 2001;108(1):35-37.
Mullur R, Liu Y, Brent G. Thyroid Hormone Regulation of Metabolism. Physiol Rev. 2014;94(2):355-382.
https://karger.com/anm/article-abstract/51/2/188/40455/Effect-of-Zinc-Supplementation-on-Thyroid-Hormone?redirectedFrom=fulltext
Thyroid Disease and the Heart | Circulation. AHA Journals. http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/116/15/1725. Accessed February 3, 2017.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1538562/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5112739/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/105899/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5112739/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6028657/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2472981/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4711001/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3712348/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4504177/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26434494/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/760253/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28577409/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25210669/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15689116/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6727359/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20352370/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4712861/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26254889/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24371036/



High PTH , low vitamin D causes insomnia
Get these tested:
-prolactin
-PTH
-Vitamin D
-Total cholesterol
-TSH
Only use blackseed oil topically- very strong oil
Get prolactin and Vitamin D tested.
Low vitamin D can wreck sleep , Iv noticed this commonly - simple fix and improvement in sleep after supplementation